In a historic moment for international diplomacy, Prime Minister Narendra Modi and summit leaders in the European Community have agreed on what they call the "Mother of All Deals." The India-European Union Free Trade Agreement (FTA), which was finalized on January 27, 2026, is the culmination of nearly twenty years of discussions. Filled with 24 chapters and a composite market of two billion people, the deal is very much not simply a trade document it is a strategic realignment at the global stage.
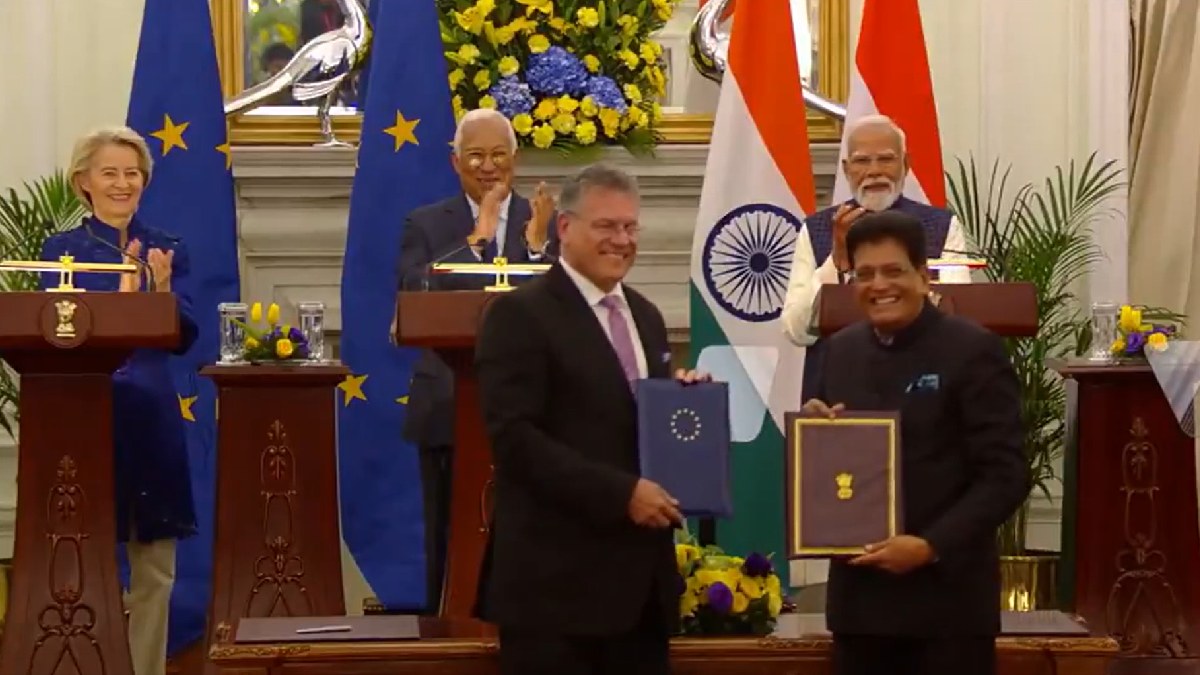

Here are 10 reasons why the India-EU FTA is a game changer for our economies and the world.
1. Strategic Defence Infusion
For the first time, India is becoming a part of the European defence landscape. The newly established Security and Defence Partnership (SDP) gives Indian businesses access to participate in the EU’s €150-billion SAFE (Security Action for Europe) programme. This will help drive joint research, development, and manufacturing of future-proof military hardware, which would lessen India’s reliance on old single-source suppliers in the long term.
2. Revolutionizing Worker Mobility
The deal creates a signature Mobility Framework for Indian professionals. By simplifying work visas and enabling legal avenues for skilled migration, it addresses Europe's acute talent shortage, while opening unprecedented access for Indian IT experts, engineers and healthcare workers to 27 countries on the path. This move broadens the range of jobs outside the mature United States and United Kingdom.
#WATCH | Delhi | PM Narendra Modi, the President of the European Commission, Ursula Von Der Leyen and the President of the European Council, António Luís Santos da Costa, witness the signing and exchange of the political declaration of the conclusion of negotiations of the… pic.twitter.com/SfT1SDjLTJ
— ANI (@ANI) January 27, 2026
3. Major Tariff Relief for Manufacture Importers
The agreement removes or substantially lowers duties on more than 90 percent of merchandise traded. For India’s labour-intensive sectors textiles, leather, footwear where tariffs hover around 10 percent, this “zero-duty” access represents a huge advance. It levels the playing field with competitors like Vietnam and Bangladesh on the lucrative European market.
4. Reducing Cost of Living for the Indian Middle Class
There will be a slow price reduction for luxury European products in India. Levies on fully constructed luxury vehicles, now as high as 110%, will be brought down to around 40 per cent at first, then to global standards. And high-end European wines and spirits will also come cheap, serving India's growing urban middle class.
5. “Friend-Shoring” Global Supply Chains
Amidst increasing geopolitical churn and trade frictions from the U.S. and China, this accord represents a “Third Pole” of stability. By aligning two of the world’s biggest democracies, the deal secures resilient supply chains for crucial parts such as integrated circuits and chemicals that, collectively, create India as a global center for so-called “trusted” manufacturing.
6. Building the Pharmaceutical System of the Globe
The FTA has a chapter on Intellectual Property and Regulatory Alignment. For Indian pharma giants, it includes simplified authorizations and quicker sales of generic medicines in continental Europe. In this way, Europe gets access to quality care at an affordable price and India solidifies its place as a pioneer in life sciences worldwide.
7. A Boost for MSMEs and Startups
By standardizing tech and cutting down on non-tariff barriers, the deal simplifies export for small and medium-size enterprises (MSMEs). A startup in Bengaluru can now follow the same set of European standards to sell to Paris, Berlin and Madrid — a new frontier that cuts “cost of compliance” that smaller players have found to be a significant deterrent.
8. Sustainability and Clean Tech
A key aspect of the deal concerns the Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM). Both powers have reached a compromise that helps India’s green transition while aligning with the EU’s climate ambition. This reinforces the transfer of European green technologies in hydrogen and solar to Indian factories.
9. Safe Digital and Cyber Trade
As negotiations for a Security of Information Agreement (SOIA) begin, the agreement opens the door for secure data transfers. It is crucial to this high-value R&D and digital services so that Indian tech companies can work with sensitive European data under the framework of a robust and mutually recognized legal framework.
10. Geopolitical Balancing Act
This partnership, which accounts for 25% of global GDP and a third of global trade, is a huge geopolitical stabilizer. It sends a message to the world that India and the EU are for rule-based rather than isolationist cooperation essentially putting both economies in a wall between themselves and the exogenous shocks brought by a trade war and one-off tariffs.